
- Blog
Comprehensive Guide to Fully Automatic Screw Locking Machines: Types, Features, and Selection Guide
- By tian81259@gmail.com
In the wave of industrial automation, fully automatic screw locking machines have become essential tools for improving assembly efficiency and reducing labor costs. With the wide variety of equipment types on the market, how can you make the right choice? This article will systematically review the mainstream types to help you make an informed decision!
Classification by Structure and Application Mode
1.Multi-Axis Automatic Screw Locking Machine
Principle: Equipped with multiple electric screwdrivers (main spindles), customized based on the screw hole layout of the product.
Features: Extremely high efficiency (locks multiple screws simultaneously), good stability, designed for specific applications.
Suitable for: Mass production with standardized products, where screw hole positions are fixed (e.g., circuit boards, appliance housings, mounting brackets).
Limitations: Low flexibility; product changeover requires adjustment or replacement of fixtures/spindle positions. Higher initial investment.
2.Coordinate-Type (Robot/Platform) Automatic Screw Locking Machine
Principle: Driven by a motion platform (XYZ three-axis or more), precise positioning of one or multiple electric screwdrivers.
Features: Excellent flexibility (program-controlled paths), strong adaptability (different hole positions, various products), high positioning accuracy.
Suitable for: Multi-variety, small-batch, or products with complex, varying screw hole positions (e.g., smartphones, smart devices, automotive electronic parts, toys).
Types:
- Single Head: One electric screwdriver, locks screws sequentially.
- Multi-Head: Multiple electric screwdrivers working collaboratively or independently, achieving efficiency close to multi-axis machines with better flexibility.
- Robot-Mounted: A robotic arm holding the screwdriver for greater flexibility and a larger operational range.
Classification by Feeding and Locking Function Integration
1.Classification by Feeding and Locking Function Integration
Principle: The automatic screw feeder (often air-blown or vacuum-based) and the locking mechanism are highly integrated into the same machine body.
Features: Compact structure, small footprint, short feeding path, high stability.
Suitable for: Most applications, especially in space-limited or high-stability environments.
2.Separate Automatic Screw Locking Machine
Principle: The screw feeder and locking execution mechanism (e.g., multi-axis head, coordinate platform, or robot) are physically separated, connected via feeding tubes.
Features: Flexible layout, feeders can be placed away from the main unit (ideal for vibration or high-temperature environments), one feeder can serve multiple locking heads.
Suitable for: Special environmental requirements, long-distance feeding, or centralized feeding with distributed locking scenarios.
Classification by Equipment Shape and Installation Mode
1.Desktop Automatic Screw Locking Machine
Features: Compact size, lightweight, can be placed on a workbench.
Suitable for: Small parts, laboratories, repair stations, lightweight production, or space-constrained environments.
2.Vertical/Floor-Type Automatic Screw Locking Machine
Features: Independent machine body, stable placement on the floor, more robust structure, accommodates larger operational range and multi-axis systems.
Suitable for: Medium to large parts, standard production lines, environments requiring high stability and large production capacity (most common type).
Classification by Screw Feeding Method
1.Air-Blown Feeding (Mainstream)
Principle: Compressed air blows screws through pipes to the screwdriver.
Features: Fast speed (especially suitable for small screws), longer transmission distance, relatively simple structure.
Suitable for: Screws smaller than M5, where screws do not easily tangle or jam. Requires high consistency in screw size, thread, and washers.
2.Vacuum Feeding (Pick-Up Type)
Principle: The screwdriver head is equipped with a vacuum nozzle that directly picks up screws from a pre-arranged material tray or track and moves them to the hole for fastening.
Features: More precise positioning, less chance of screw misalignment or floating lock, ideal for irregular screws or those with washers, and those prone to jamming.
Suitable for: Larger screws (M3 and above), special screws (long screws, screws with washers/gaskets), high-precision fastening environments. Speed is generally slightly slower than air-blown feeding.
Classification by Intelligence and Integration Level
1.Basic Automatic Screw Locking Machine
Functions: Automatically feeds screws, locks them, and performs basic checks (e.g., torque, thread slipping, floating lock).
Suitable for: Standard locking needs.
2.Intelligent Automatic Screw Locking Machine
Functions: Builds on the basic model with additional features:
- Visual positioning system (for correction and complex alignment)
- Data traceability (MES/SCADA integration)
- Deep process monitoring (locking curve analysis)
- Adaptive control, enhanced error-proofing.
Suitable for: High precision requirements, flexible mixed-line production, data-driven management, and key quality control points.
How to Choose the Most Suitable Fully Automatic Screw Locking Machine?
When selecting, consider the following key factors:
- Product Characteristics: Size, material, number of screw holes, positions and distribution (regular/irregular), screw specifications (type, size, material, with or without washers)?
- Production Capacity Requirements: Cycle time requirements (seconds per piece or parts per minute)? Production volume (high-volume continuous production or small-batch multi-product)?
- Precision Requirements: How precise is the screw hole positioning and locking depth/torque? Is visual assistance needed?
- Automation Integration: Does the machine need to operate independently, or should it integrate with a production line, robotic arms, or AGVs?
- Budget: Price differences exist between various types and configurations.
- Space Availability: Are there any space limitations for equipment installation?
Conclusion:
The types of fully automatic screw locking machines are diverse, ranging from highly efficient, specialized multi-axis machines to flexible, versatile coordinate or robotic types, with different feeding methods (air-blown/vacuum) and forms (desktop/floor-mounted). Each type has its unique advantages and applicable scenarios. Understanding these categories and their core features is key to successfully introducing an automated locking solution and achieving cost reduction and efficiency improvement goals.
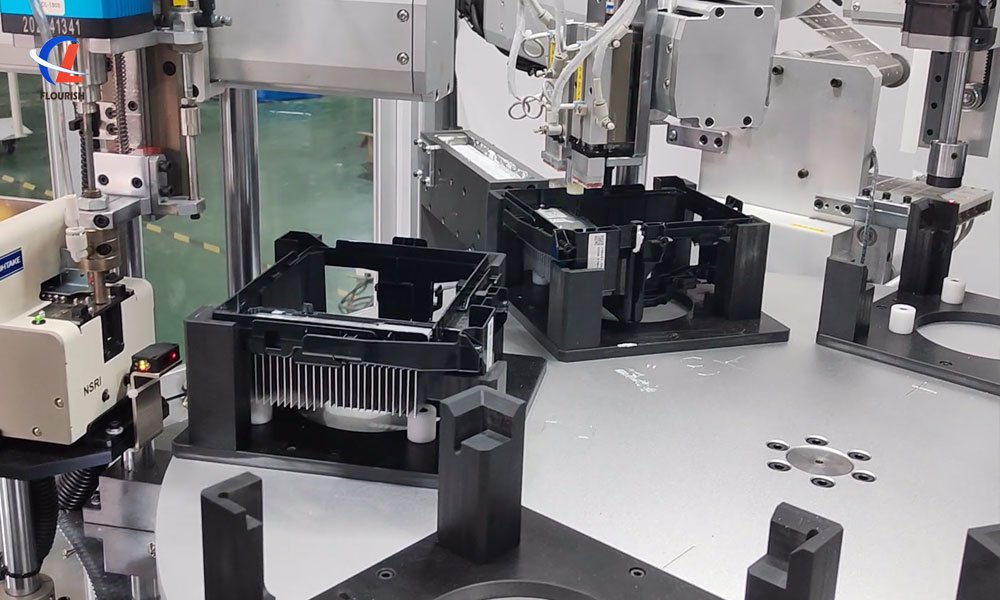
Heatsink Locking for Small Appliance Products – Work Scenario
Flourishe has been deeply involved in the automation of transistor heatsink screw fastening for 20 years, offering a full range of solutions from multi-axis and coordinate-based systems to robotic fastening systems. We have a professional team ready to tailor the best solution for your product characteristics and production needs, and we also provide free consultations and sample testing services!
Related Posts
20 Years of Expertise, Trusted by Clients Worldwide
The Preferred Choice of Foxconn, BYD, and Huawei




