- Blog
Electronic Components and Their Functions — A Practical Guide for Power-Electronics Manufacturing
- By tian81259@gmail.com
Electronic Components and Their Functions — A Practical Guide for Power-Electronics Manufacturing
Reading time: ~8 minutes
When we talk about electronic components and their functions, most guides stop at theory. This article goes further for manufacturers of power supplies, adapters, LED drivers, EV charging inverters, and industrial power modules. You’ll learn not only what each component does, but also how precise lead forming and cutting directly improve assembly quality, speed, and long-term reliability—and which Flourishe machines fit typical use cases.
- Component Basics: What Each Part Does
- Why Lead Forming Matters in Real Production
- Quick Reference: Components × Functions × Recommended Machines
- DFM Tips: Tolerances, Pitch, Foot Length & Insertion
- How to Choose the Right Forming Machine
- Use Cases in Power-Electronics Lines
- Next Steps
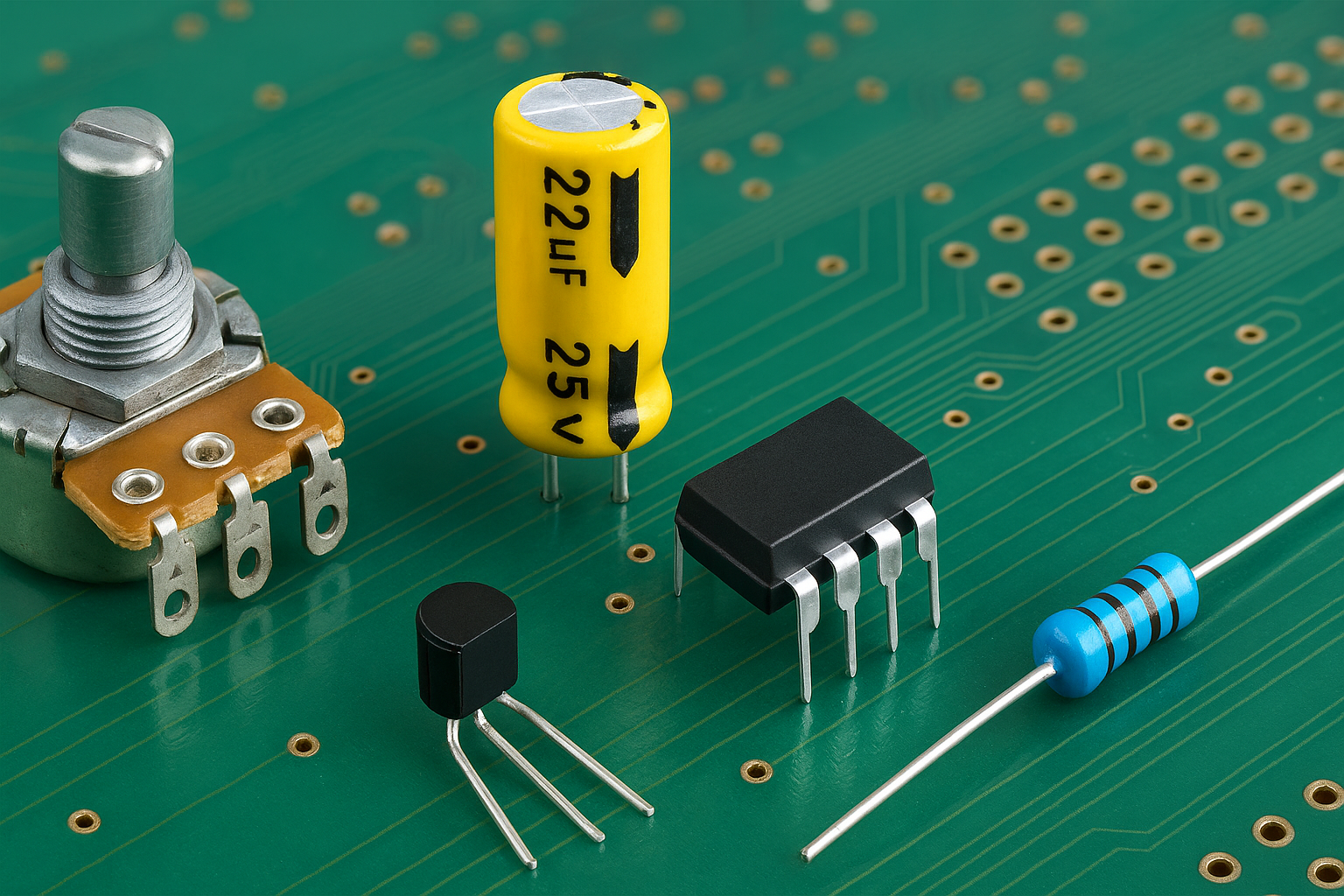
Component Basics: What Each Part Does
Below are the most common components in power-electronics production, explained simply and practically.
Resistors
Function: Control current, set bias, divide voltage, and stabilize circuits. In power supplies, they also serve as inrush limiters and bleeder paths.
Manufacturing note: Axial or radial leads often need consistent foot length and repeatable 90° bends for wave-solder or selective-solder fixtures. Precision forming avoids tombstoning, skew, and solder bridges.
Resistor Forming Machines: Precision Cutting & Bending
Capacitors (Electrolytic, Film, Ceramic)
Function: Store and filter energy (bulk, smoothing, decoupling), set timing (RC), and tune power factor or EMI filtering.
Manufacturing note: Consistent lead spacing and height keep caps stable through soldering and vibration. Clean, burr-free lead cutting prevents solder wicking and micro-cracks at the pad.
FL-805 Belt-Type Radial Capacitor Lead Cutter · FL-816 Tape-Fed Radial Lead Cutting / Forming · FL-803 Automatic Bulk Capacitor Lead Cutter · FL-810 Pneumatic Bulk Capacitor Former
Diodes & Rectifiers
Function: One-way conduction (rectification, flyback, protection). In SMPS, diode placement and thermal path are critical.
Manufacturing note: Precise axial forming reduces stress on the epoxy body and ensures perfect seating in jigs.
Axial & Radial Lead Cutting/Forming Solutions
Transistors / MOSFETs / IGBTs
Function: Switching and amplification. Power stages rely on low RDS(on), proper gate drive, and robust thermal coupling.
Manufacturing note: For TO-220/TO-247 and power modules, screw fastening with thermal paste and insulation pads must be consistent to avoid hot spots and early failures.
FL-915A Transistor Heatsink Forming & Fastening · FL-950 Transistor Lead Former · Transistor Heatsink Assembly Machine (Category)
Inductors & Transformers
Function: Energy storage, filtering, isolation. Mechanical stability is essential—tall parts need uniform lead forming to resist vibration.
Radial Lead Forming Machines (Category)
ICs & Optocouplers
Function: Control, feedback, and protection. Isolation devices (optocouplers) maintain safety boundaries.
Manufacturing note: For DIP parts, kinked leads can improve retention before solder; lead length control reduces solder voids.
Connectors, Switches, Relays
Function: I/O, power entry, control. These often define the board’s mechanical fit—accurate forming ensures panel alignment.
Component Lead Cutting & Forming (All)
Why Lead Forming Matters in Real Production
- Repeatability = Quality: Tight control of pitch, foot length, and bend angle ensures consistent solder fillets and reliable AOI results.
- Speed without Scrap: Automated forming and cutting reduce rework, bent bodies, and pad lift, while keeping cycle time predictable.
- Fixture Fit: Properly formed leads drop into wave/selective fixtures with less operator manipulation—fewer placement errors, less fatigue.
- Reliability: Correct strain relief prevents micro-cracks at the body-lead interface and improves vibration endurance.
Explore our Manufacturing Solutions to match forming stages with your soldering and testing workflow.
Quick Reference: Components × Functions × Recommended Machines
| Component | Primary Function | Lead Style | Typical Forming Need | Recommended Flourishe Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor (axial) | Current/voltage control | Axial | 90° bend, fixed foot length | Resistor Forming Machines (Guide) |
| Capacitor (radial/electrolytic) | Energy storage & filtering | Radial | Lead cutting, pitch & height control | FL-805 Cutter / FL-810 Former |
| Diode | Rectification / protection | Axial | Consistent bends, body protection | Axial/Radial Lead Cutting & Forming |
| Inductor / Transformer | Energy storage / isolation | Radial / custom | Stability, vibration resistance | Radial Lead Forming Machines |
| MOSFET / IGBT | Power switching | TO-220/TO-247/module | Thermal paste + insulation + heatsink fastening | FL-915A Heatsink Assembly |
DFM Tips: Tolerances, Pitch, Foot Length & Insertion
- Pitch (P): Match component lead spacing to PCB pad spacing with ±0.1–0.3 mm tolerance to avoid pad stress.
- Foot Length (FL): Keep consistent insertion depth; over-long leads cause solder icicles, too-short leads risk poor wetting.
- Bend Radius: Aim for ≥ the lead diameter to reduce stress at the body interface.
- Height Control: Especially for electrolytics and magnetics; uniform height improves AOI and airflow.
- Clean Cuts: Burr-free ends reduce solder wicking and flux entrapment.
See our practical overviews: Resistor Forming Guide and Radial Capacitor Forming Guide.
How to Choose the Right Forming Machine
- Component mix: Axial vs radial ratios, body sizes, and top-10 SKUs by volume.
- Downstream process: Wave, selective, or hand solder? Fixture or inline insertion?
- Quality targets: IPC standards, AOI criteria, allowable lead length/angle tolerances.
- Cycle time & staffing: Decide auto vs semi-auto vs manual. Start with semi-auto then scale.
- Changeover frequency: Prefer quick-change tooling and recipe memory if SKUs change often.
Compare models in our lead cutting & forming catalog or explore Solutions for line design ideas.
Use Cases in Power-Electronics Lines
1) LED Driver / Adapter Lines
High-volume radial capacitors + axial resistors often dictate takt time. Pair an FL-816 for tape-fed radial parts with an axial resistor forming setup to stabilize insertion and reduce solder defects.
2) Industrial Power & EV Charger Modules
Thermal reliability dominates. Use FL-915A heatsink assembly for repeatable paste application, insulation placement, and screw torque, ensuring safe junction temperatures and longer MTBF. For related topics, see this overview of heatsink screw-locking automation.
3) Repair & Low-Volume / High-Mix
For labs and NPI cells, the FL-805 belt-type cutter offers fast, precise trimming without setting up a full auto line—perfect for prototypes and small batches.
Next Steps
If you’re optimizing yield, speed, or long-term reliability, aligning component functions with the right forming and fastening processes is the fastest win. Explore our Solutions, browse Lead Cutting & Forming Machines, or review the Transistor Heatsink Assembly lineup. Prefer a quick consult? Use the Get a Quote form on any product page to reach our team.
Related Posts
20 Years of Expertise, Trusted by Clients Worldwide
The Preferred Choice of Foxconn, BYD, and Huawei




